The Loire Estuary area in Atlantic France has just been awarded a special label by Ademe (the French Environment and Energy Management Agency), which launched the Low Carbon Industrial Zone (ZIBaC) call for projects as part of the “France 2030” programme.
The consortium, which is made up of the Association of Loire Estuary Industrialists (bringing together Arcelormittal, Cargill, EDF, Elengy, Engie, Eqiom, TotalEnergies, and Yara), the Saint-Nazaire Agglomération, the Community of Communes Estuaire et Sillon, Nantes Saint-Nazaire Port, and the Atlantic France regional council, is proposing around thirty concrete actions to accelerate the decarbonisation and energy transition of this industrial region. Among these actions, hydrogen will be of great importance in the decarbonisation project; there will be opportunities for new infrastructures to be built, for manufacturers, and the ongoing development of hydrogen usage.
Zibac: heading towards a low-carbon energy hub
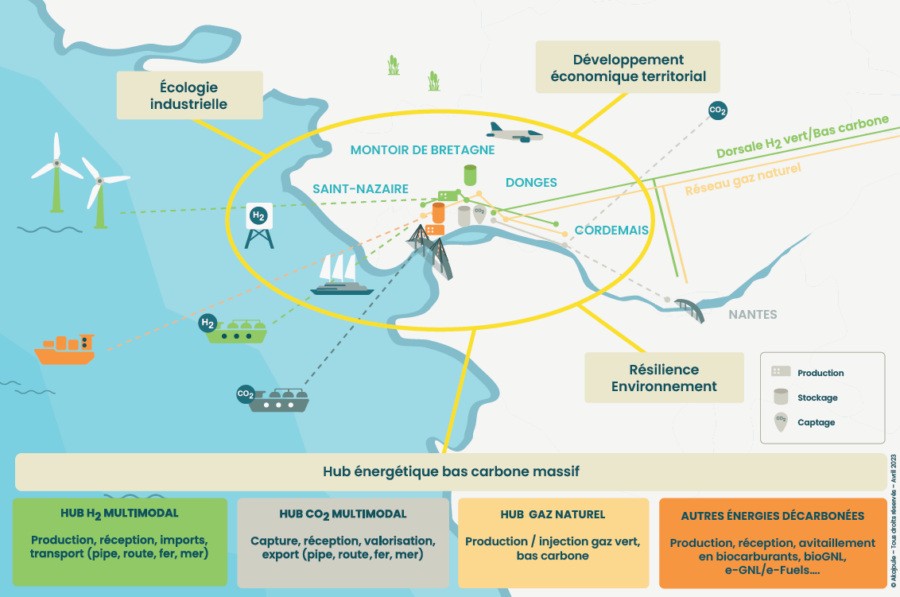
A common ambition and roadmap have been drawn up, with the threefold aim of achieving carbon neutrality in the port area by 2050, enabling industrial resilience in the face of the foreseeable consequences of climate change, and encouraging the emergence of new sectors, such as hydrogen, which will support the energy transition.
The €8.2 million action programme has been planned for a 2-year period and is supported by up to €4.1 million from Ademe. It aims to accelerate the transformation of this industrial port area (which already provides 28,500 jobs) into a hub for great quantities of decarbonised energies through the development of infrastructure in order to align the producers with the emerging and future needs of France. Some examples of the planned actions to be taken are:
- A multimodal hydrogen hub for the production, importation, and transportation of low-carbon hydrogen
- A multimodal CO2 hub for the capturing, reception, recovery, and exportation of industrial CO2
- A natural gas hub for the production and distribution of green/low-carbon gas
- A hub dedicated to other low-carbon energies for the production and refuelling of biofuels, bioNGL, etc
The other areas of work focus on themes linked to industrial ecology (setting up local electricity loops produced from renewable energies, a heating network, developing biomass, or decarbonising industrial processes and port flows) and environmental resilience: how to adapt to climate change and how to collectively improve water management.
This approach will support the decarbonisation projects of manufacturers who have committed to a voluntary trajectory to become “net zero” by 2050, by building on synergies between local players and enhancing the economic attractiveness of the area.
The Loire Estuary Decarbonisation Association (ADELE), which was set up by the five founding partners, will spearhead this collective decarbonisation drive (which has already demonstrated its ability to reinvent itself) in the Loire area.
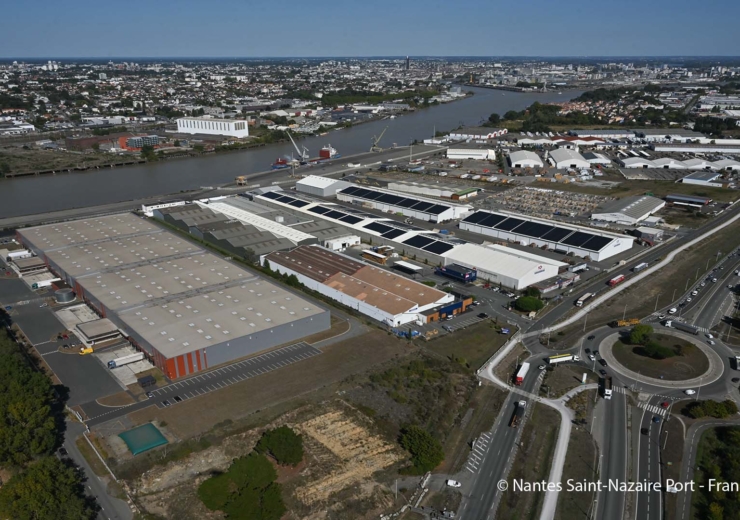
The Loire Estuary: a land of industry
With the leading port on the Atlantic seaboard (30 million tonnes of goods a year), its close proximity to offshore wind farms (the first offshore wind farm with a capacity of 480 MW, the first floating wind turbine, a global potential of 20 GW), and with direct access to international markets, the Loire Estuary region is a major energy hub. It provides 10% of France’s energy supply, is a manufacturing and technology industrial base comprising several world leaders (28,500 jobs and 500 companies), was awarded the “Territoire d’Industries” label in 2018, and has a vibrant, well-established public-private partnership DNA. 5.9 million tonnes of CO2 are emitted annually in the region, 85% of which are generated by the players involved in the ZIBaC Loire Estuary Project.
The ZIBaC approach
In the spring of 2022, the French Environment and Energy Management Agency (Ademe) launched the ZIBaC call for projects. Through this initiative, the French government aims to support industrial regions in their ecological and energy transformations and to accelerate the decarbonisation of France’s main industrial basins in order to improve both their competitiveness and attractiveness and to support the recovery of their economic activity.


 Français
Français